Traditionally, production management involves planning, scheduling, and overseeing the movement of goods throughout the manufacturing process. It required meticulous coordination, manual supervision, and extensive data tracking to ensure efficiency and quality. However, with increasing complexity in global supply chains and customer demand for customization, the limitations of manual oversight have become more apparent.
Enter AI and automation, technologies that are now integral to smart manufacturing environments.
Key Ways AI and Automation Are Changing Production Management
AI and automation are revolutionizing production management by enhancing efficiency, enabling real-time decision-making, and fostering greater agility across manufacturing operations.
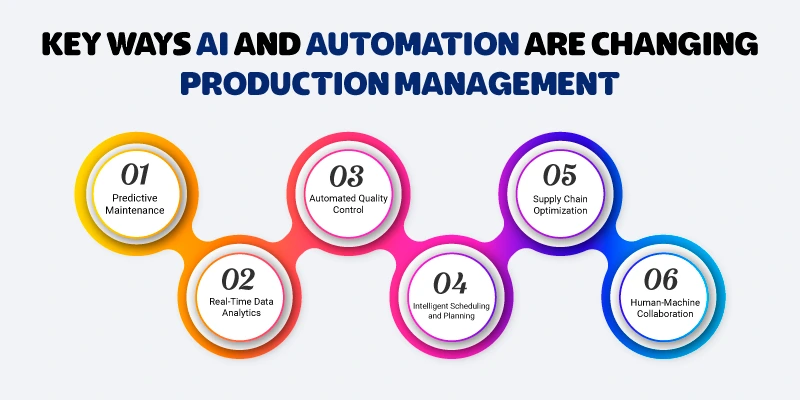
1. Predictive Maintenance
One of the most transformative applications of AI is in predictive maintenance. Rather than waiting for equipment to fail and cause costly downtime, AI algorithms analyze data from sensors embedded in machinery to predict when a part is likely to break down. This allows managers to schedule maintenance proactively, reducing unplanned downtime by up to 50% and extending equipment life.
2. Real-Time Data Analytics
AI-powered systems continuously monitor production lines, collecting data on machine performance, product quality, and operator efficiency. These systems use real-time analytics to identify bottlenecks, deviations, or inefficiencies immediately. Managers can then respond faster and make informed decisions to keep production running smoothly.
3. Automated Quality Control
Computer vision, a branch of AI, is increasingly used in quality inspection. High-resolution cameras combined with machine learning can detect defects in products more accurately and quickly than human inspectors. This ensures consistent quality and reduces waste due to human error.
4. Intelligent Scheduling and Planning
AI can dynamically optimize production schedules based on factors such as inventory levels, order priorities, and equipment availability. Unlike traditional ERP systems, AI-driven scheduling tools adapt in real-time to unexpected disruptions (e.g., a delayed shipment or machine malfunction), minimizing downtime and improving throughput.
5. Supply Chain Optimization
Production management doesn’t exist in isolation; it’s deeply connected to the supply chain. AI helps managers forecast demand more accurately, identify optimal sourcing strategies, and adjust production levels in response to market changes. Machine learning models can detect supply chain risks (like delays or shortages) before they impact production.
Here understanding the Factors To Consider When Procuring Goods Or Services Globally can help you make informed decisions and avoid costly pitfalls.
6. Human-Machine Collaboration
Automation doesn't mean replacing humans; it means enhancing their capabilities. Collaborative robots (cobots) now work alongside human workers to handle repetitive or dangerous tasks, improving workplace safety and freeing workers to focus on more complex responsibilities. AI also powers intuitive human-machine interfaces, making it easier for operators to interact with smart systems.
Benefits of AI and Automation in Production Management
The integration of AI and automation into production management offers a range of strategic and operational benefits that are reshaping how modern factories operate. These technologies do more than streamline workflows; they transform the decision-making process, enhance flexibility, and future-proof operations in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
1. Increased Operational Efficiency
AI algorithms optimize every stage of the production process, from scheduling and inventory management to machine utilization and quality control. Automated systems perform repetitive tasks with precision and speed, reducing cycle times and eliminating human errors. The result is a more streamlined operation with higher throughput and consistent quality.
2. Predictive Maintenance and Reduced Downtime
One of the most impactful uses of AI is in predictive maintenance. By analyzing data from sensors embedded in machines, AI can detect subtle patterns that indicate wear and tear or impending failure. This allows maintenance teams to service equipment before breakdowns occur, avoiding costly downtime and extending the life of machinery.
3. Real-Time Visibility and Analytics
AI and automation provide managers with real-time data dashboards that offer visibility into every aspect of production, from raw material input to finished goods output. These insights help identify bottlenecks, optimize workflows, and make faster decisions based on live operational data.
4. Improved Product Quality and Consistency
Automated quality control systems, such as computer vision powered by AI, inspect products for defects with unmatched accuracy and consistency. These systems can operate 24/7 without fatigue, ensuring that only products that meet strict quality standards are released.
5. Enhanced Supply Chain Coordination
AI plays a vital role in connecting production with the broader supply chain. By analyzing historical data, demand trends, and external factors (such as market conditions or weather patterns), AI helps forecast demand more accurately and plan production accordingly. This reduces excess inventory, minimizes stockouts, and improves on-time delivery rates.
6. Labor Optimization and Workforce Empowerment
Rather than replacing human workers, AI and automation enhance their capabilities. Automation takes over routine and hazardous tasks, allowing workers to focus on higher-value responsibilities such as quality assurance, process optimization, and innovation. Meanwhile, AI-driven tools assist decision-making, making it easier for teams to manage complexity.
7. Cost Reduction
Through reduced downtime, minimized waste, better inventory management, and more efficient resource use, AI and automation contribute significantly to lowering overall production costs. Over time, the return on investment (ROI) from adopting these technologies can be substantial.
Typical Savings Areas:
- Maintenance and repairs
- Energy consumption
- Labor allocation
- Material usage
8. Scalability and Flexibility
AI and automation allow manufacturers to scale operations up or down with minimal disruption. Whether it’s launching a new product, expanding production lines, or responding to seasonal demand, smart systems can adapt quickly without the need for significant manual reconfiguration.
9. Informed Decision-Making
AI-powered analytics tools provide managers with deep insights into performance metrics, production trends, and potential risks. These insights support data-driven decision-making, ensuring strategies are based on facts rather than assumptions.
10. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
AI can optimize energy consumption by adjusting machine operations based on real-time demand. Automation also supports waste reduction through precise material handling and efficient process control.
Challenges to Consider
AI and automation promise transformative benefits for production management, but their implementation is not without significant challenges. Companies need to be aware of these obstacles and prepare accordingly to ensure a successful transition.

1. High Initial Investment Costs
Implementing AI and automation technologies often requires substantial upfront capital. This includes the cost of purchasing advanced machinery, AI software licenses, sensors, and IoT devices, as well as upgrading existing infrastructure to support these technologies. For many manufacturers, especially small and medium enterprises (SMEs), these expenses can be prohibitive. Additionally, investment is needed for employee training and change management initiatives, further increasing the financial burden.
Careful understanding and planning of manufacturing costs versus production costs are essential to managing these investments effectively and ensuring a smooth transition to smarter, more automated production processes.
2. Integration with Legacy Systems
Most manufacturing facilities operate a mix of legacy equipment alongside modern machines. Integrating AI and automation with these older systems can be complex and time-consuming. Legacy systems may lack standard communication protocols or sufficient data interfaces, making it difficult to achieve seamless connectivity. Custom integration solutions are often required, which can delay deployment and increase costs.
3. Data Quality and Management
AI systems rely heavily on high-quality, consistent data to function effectively. However, many production environments struggle with fragmented, incomplete, or inaccurate data sets. Poor data quality can lead to incorrect AI predictions, reducing the effectiveness of automation and potentially causing operational disruptions. Establishing robust data collection, cleaning, and governance processes is essential but can be challenging to implement.
4. Cybersecurity Risks
As production systems become more connected through IoT and cloud platforms, they also become more vulnerable to cyberattacks. Unauthorized access, data breaches, or ransomware attacks can compromise sensitive production data or disrupt manufacturing operations. Ensuring strong cybersecurity measures, including encryption, network segmentation, and continuous monitoring, is critical but requires specialized expertise and resources.
5. Workforce Readiness and Resistance
The introduction of AI and automation often brings concerns among workers about job security and changes in roles. Resistance to new technologies can slow down adoption and reduce overall productivity. Furthermore, employees need new skills to operate and collaborate effectively with AI-driven systems. Without proper training and clear communication, companies risk facing low morale, high turnover, or skill gaps that hinder the full benefits of automation.
6. Change Management Complexity
Shifting to AI-driven production management represents a major organizational change. It requires aligning processes, culture, and goals across multiple departments. Poorly managed change initiatives can lead to confusion, duplicated efforts, or misaligned objectives. Effective leadership, clear communication, and phased implementation strategies are necessary to manage this complexity successfully.
7. Ethical and Legal Considerations
The use of AI raises important ethical questions around data privacy, transparency, and accountability. Manufacturers must ensure that AI algorithms are fair and unbiased, especially when they impact workforce decisions. Additionally, compliance with regulations related to data protection, labor laws, and industry-specific standards can add layers of complexity to AI deployments.
8. Scalability and Flexibility Challenges
While AI and automation offer scalability benefits, implementing these solutions at scale can expose technical limitations or unforeseen bottlenecks. Customizing AI systems to handle diverse product lines, fluctuating demand, or changing regulatory requirements requires ongoing development and support. Failure to design flexible systems can limit long-term benefits and adaptation.
The Future of Production Management
Looking ahead, we can expect even deeper integration of AI with emerging technologies like digital twins, edge computing, and 5G. These will further enhance visibility, responsiveness, and customization in manufacturing environments. Additionally, generative AI could begin to play a role in designing production processes or automatically generating responses to production anomalies.
Ultimately, the companies that embrace AI and automation early and invest in aligning technology with human talent will be best positioned to lead in the era of smart manufacturing.
SIXM: Your Partner in Smart, Agile Production
At SIXM, we believe the future of manufacturing lies in the seamless integration of AI and automation with human expertise. These technologies are not just tools; they are catalysts for a smarter, more agile, and innovative production environment. While the path to transformation comes with challenges, it also offers unprecedented opportunities to enhance efficiency, ensure quality, and drive sustainable growth.
By partnering with SIXM, manufacturers can confidently navigate this evolution, harness cutting-edge solutions, and build resilient operations that thrive in today’s fast changing world. As leading Procurement & Sourcing Specialists, we support businesses in optimizing their supply chains to complement intelligent production management. Embrace the power of intelligent production management with SIXM and lead your industry into the future.