Supplier Quality Engineers (SQEs) are the bridge between OEM expectations and supplier capabilities. By deploying structured quality tools, ensuring process consistency, and driving continuous improvement, SQEs play a vital role in preventing defects and building long-lasting, reliable products.
Companies rely heavily on external suppliers for critical components, subassemblies, and materials. While this allows businesses to reduce costs and scale efficiently, it also introduces potential risks; particularly around product quality and reliability. Supplier Quality Engineers (SQEs) ensure that suppliers meet performance expectations and that the final product is consistent, compliant, and reliable.
In this blog, we explore the role of SQEs, how they drive product reliability, and the key strategies they use to ensure supplier performance.
What Does a Supplier Quality Engineer Do?
Supplier Quality Engineers act as a bridge between an organization and its suppliers. Their primary responsibilities include:
- Evaluating and qualifying suppliers
- Conducting audits and inspections
- Monitoring supplier performance
- Managing non-conformances and corrective actions
- Supporting new product introductions (NPI)
- Driving continuous improvement initiatives
By actively engaging with suppliers at every stage of the production process, SQEs help prevent quality issues before they arise and ensure that any deviations are quickly addressed.
The Link Between SQEs and Product Reliability
Product reliability refers to the ability of a product to perform consistently over its expected lifetime. Defective or inconsistent components from suppliers can directly affect this reliability, leading to increased warranty claims, product recalls, and damage to brand reputation.
SQEs safeguard product reliability through:
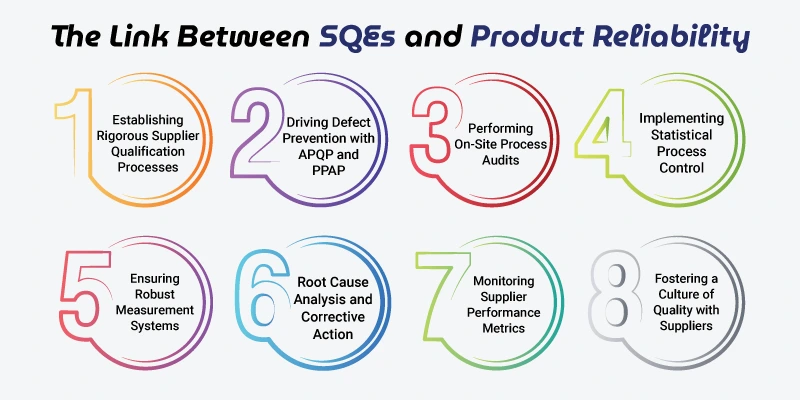
1. Establishing Rigorous Supplier Qualification Processes
Reliability starts with choosing the right suppliers. SQEs conduct thorough evaluations before a supplier is approved to deliver critical components. These evaluations include:
- Technical capability assessments
- Audits of quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001, IATF 16949)
- Sample part testing and process validation
- Historical performance reviews
By setting a high bar for entry, SQEs ensure that only capable and committed suppliers become part of the supply chain—reducing the risk of future quality issues.
2. Driving Defect Prevention with APQP and PPAP
SQEs actively participate in product development through tools like Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP) and Production Part Approval Process (PPAP). These frameworks are designed to build quality into the product from the earliest stages.
SQEs work closely with suppliers to:
- Develop robust process flows and control plans
- Conduct risk assessments (FMEA) to prevent failures
- Validate prototype and production samples
- Ensure consistency through process capability studies
This proactive approach minimizes variation, controls risks, and sets the stage for long-term product reliability.
3. Performing On-Site Process Audits
Supplier Quality Engineers frequently visit supplier sites to audit manufacturing processes. They evaluate:
- Process control effectiveness
- Equipment calibration and maintenance practices
- Operator training and competency
- Handling and packaging procedures
Audits identify weaknesses that could lead to reliability failures, such as contamination, improper assembly, or unstable processes. By enforcing corrective actions and continuous improvement plans, SQEs ensure that suppliers maintain consistent performance over time.
4. Implementing Statistical Process Control (SPC)
To monitor consistency, SQEs often use Statistical Process Control (SPC) techniques. By analyzing real-time production data, they can detect process drift, identify root causes, and intervene before defects occur.
Common SPC tools include:
- Control charts (X-bar, R, p-charts)
- Process capability indices (Cp, Cpk)
- Trend analysis for defect patterns
Stable and capable processes produce fewer out-of-spec parts, contributing directly to better reliability in the end product.
5. Ensuring Robust Measurement Systems (MSA)
Reliable inspection processes are critical for identifying non-conforming parts. SQEs conduct Measurement System Analysis (MSA) to confirm that suppliers’ measurement tools and inspection methods are accurate, repeatable, and reproducible.
By verifying that parts are measured correctly every time, SQEs eliminate one of the most common sources of reliability problems—misjudged or overlooked defects.
6. Root Cause Analysis and Corrective Action (RCCA)
When failures do occur—whether in the field or during manufacturing—SQEs are instrumental in identifying the root cause and driving corrective action. Using methods such as:
- 5 Whys
- Fishbone (Ishikawa) diagrams
- 8D problem solving
They ensure that not only is the issue fixed, but similar problems are prevented in the future. This long-term approach reduces recurrence and reinforces product reliability across the supply chain.
7. Monitoring Supplier Performance Metrics
SQEs maintain a performance dashboard for suppliers, tracking key metrics like:
- Defect rate (PPM)
- On-time delivery
- Audit results
- Corrective action responsiveness
By continuously analyzing this data, they identify underperforming suppliers and work with them to improve or replace them if necessary. This ongoing oversight helps maintain a reliable supplier base and minimizes production disruptions.
8. Fostering a Culture of Quality with Suppliers
Perhaps most importantly, SQEs influence the supplier’s culture. They don’t just enforce compliance; they build partnerships focused on shared goals: zero defects, continuous improvement, and long-term reliability. Through regular communication, training, and collaborative quality initiatives, SQEs help suppliers align with the manufacturer’s expectations and build quality ownership into their daily operations.
To stay competitive in today’s dynamic market, businesses must leverage the essential elements of supply chain intelligence to enhance visibility and drive smarter operations.
Key Tools & Techniques Used by SQEs
To ensure product reliability, SQEs use a variety of tools and frameworks, including:
- FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis): Identifies potential failure points and helps prioritize actions.
- SPC (Statistical Process Control): Monitors process stability and variation in production.
- 8D Problem Solving: A structured method for resolving complex quality issues.
- Control Plans: Detailed documents that specify inspection and control methods throughout the production process.
- Gauge R&R (Repeatability and Reproducibility): Ensures measurement systems are reliable.
Tools Used by SQEs
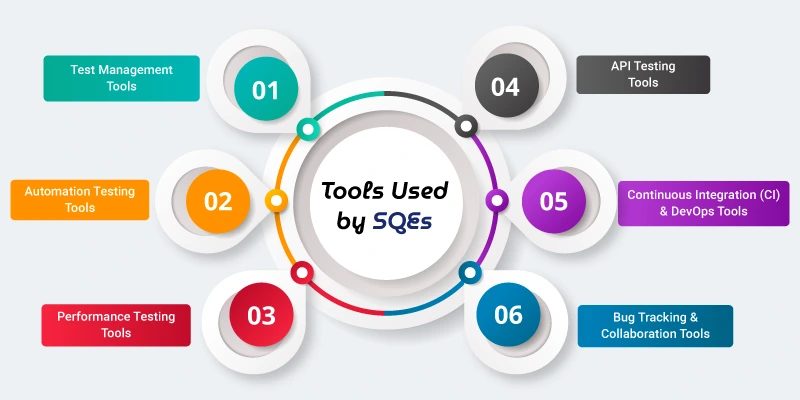
1. Test Management Tools
- JIRA + Zephyr / Xray / TestRail – For managing test cases, test cycles, and traceability.
- HP ALM / Quality Center – Comprehensive test management and defect tracking.
2. Automation Testing Tools
- Selenium / WebDriverIO / Cypress – Browser automation for web application testing.
- Appium – Mobile app testing (iOS and Android).
- TestComplete / Ranorex – For GUI test automation across platforms.
- Playwright – Modern automation for fast, reliable testing of web apps.
3. Performance Testing Tools
- JMeter – Load and stress testing for web applications.
- LoadRunner – Enterprise-grade performance testing.
- Gatling / k6 – Modern performance testing tools for DevOps workflows.
4. API Testing Tools
- Postman / Insomnia – Manual and automated API testing.
- SoapUI / RestAssured – Automated functional testing for APIs.
5. Continuous Integration (CI) & DevOps Tools
- Jenkins / GitLab CI / CircleCI – Automating builds and test executions.
- Docker / Kubernetes – Environment setup for consistent testing.
- SonarQube – Static code analysis and technical debt tracking.
6. Bug Tracking & Collaboration Tools
- JIRA / Bugzilla / Mantis – For reporting and managing software defects.
- Slack / Microsoft Teams / Confluence – Team communication and documentation.
Benefits of Strong Supplier Quality Engineering
Supplier Quality Engineering (SQE) is the discipline of ensuring that purchased components and materials meet a company’s specifications before they enter production. In industries like automotive, aerospace, electronics, and manufacturing, SQE is critical: it maintains product quality, ensures compliance with regulatory standards, and helps avoid costly disruptions. A robust SQE program empowers organizations to improve product quality, reduce operating costs, and foster stronger supplier partnerships, among other benefits.
Improving Product Quality
Strong SQE processes such as supplier audits, first-article inspections, and strict incoming material checks ensure that parts consistently meet specifications. By catching defects early at the supplier level, companies build consistent quality into their products and prevent problems on the assembly line. For example, standardized quality checks on raw materials lead to fewer production defects and higher customer trust in the final products. In industries like aerospace and medical devices, where uniform quality and reliability are paramount, strong SQE is especially beneficial.
Reducing Costs
Effective SQE cuts costs by preventing expensive quality failures. When suppliers adhere to quality standards, scrap, rework, and waste are minimized. By detecting issues early, companies avoid the high expense of product recalls, warranty repairs, and unscheduled downtime. For instance, Dell’s close collaboration with its suppliers using just-in-time delivery and joint design reviews – yielded significant cost savings and streamlined operations. In the long run, these measures translate into higher profitability and more competitive pricing.
Strengthening Supplier Relationships
A strong SQE initiative builds trust and collaboration with suppliers. Open communication about quality expectations and joint problem-solving turns vendors into strategic partners. Quality teams often work together with suppliers on corrective actions and continuous improvement, fostering transparency and accountability. In practice, involving suppliers in quality planning and feedback loops simplifies audits and approvals, creating smoother working relationships. As a result, suppliers become more responsive and aligned with the company’s needs, improving overall flexibility.
Enhancing Supply Chain Reliability
SQE improves supply chain consistency and resilience by proactively managing risk. Continuous monitoring of supplier quality metrics (such as defect rates or on-time delivery) gives companies visibility into potential issues before they become problems. With this advance notice, organizations can qualify backup suppliers or adjust production plans to avoid disruptions. Research shows that proactively managing supplier quality “reduces unexpected supply chain disruptions and ensures business continuity”. In manufacturing, where a late or defective shipment could halt an entire assembly line, this reliability is crucial.
Enabling Innovation
Collaborating closely with suppliers on quality and design can spark innovation. Involving suppliers early in product development allows them to contribute ideas for new materials, processes, or components. As one industry source observes, treating innovation as a shared goal with suppliers can lead to “groundbreaking” results. For example, Dell integrated suppliers into its R&D process, allowing them to co-design modules and anticipate demand. This deep partnership not only delivered cost savings but also helped Dell achieve rapid product innovation and faster time-to-market.
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
SQE also helps companies stay in line with regulations and standards. Industries like aerospace (AS9100) and automotive (IATF 16949) require suppliers to meet strict quality and safety criteria. A robust SQE program enforces these requirements through certifications and audits, so components are always compliant. Being proactive in supplier monitoring makes it far easier to remain compliant with evolving rules. In turn, companies reduce the risk of non-conformance that could trigger costly fines or recalls, safeguarding their brand and market access.
Supporting Data-Driven Decisions
Strong SQE generates valuable data on supplier performance, enabling data-driven decisions. By tracking metrics like defect rates, delivery performance, and corrective actions, companies can identify trends and focus improvement efforts where they matter most. Quality management software often provides dashboards and scorecards that highlight top-performing suppliers and flag emerging issues. As one quality expert notes, “More data = better quality procurement decisions,” leading to reduced lead times and waste. Over time, this data-driven approach makes it easier to identify reliable suppliers and continuously improve the supply network.
Sustainable Sourcing Alignment
As Supplier Quality Engineers help enforce standards and build reliable supplier relationships, they also support organizations in embracing sustainable sourcing practices that align quality with environmental responsibility.
How SIXM Delivers Trust Through Supplier Quality Engineering
Partnering with a Top-Rated Procurement Company like SIXM ensures that your supply chain is supported by trusted suppliers and driven by quality excellence. Through strategic supplier collaboration, rigorous quality standards, and a relentless focus on continuous improvement, they enable us to deliver the consistency, precision, and trust our customers depend on without compromise.